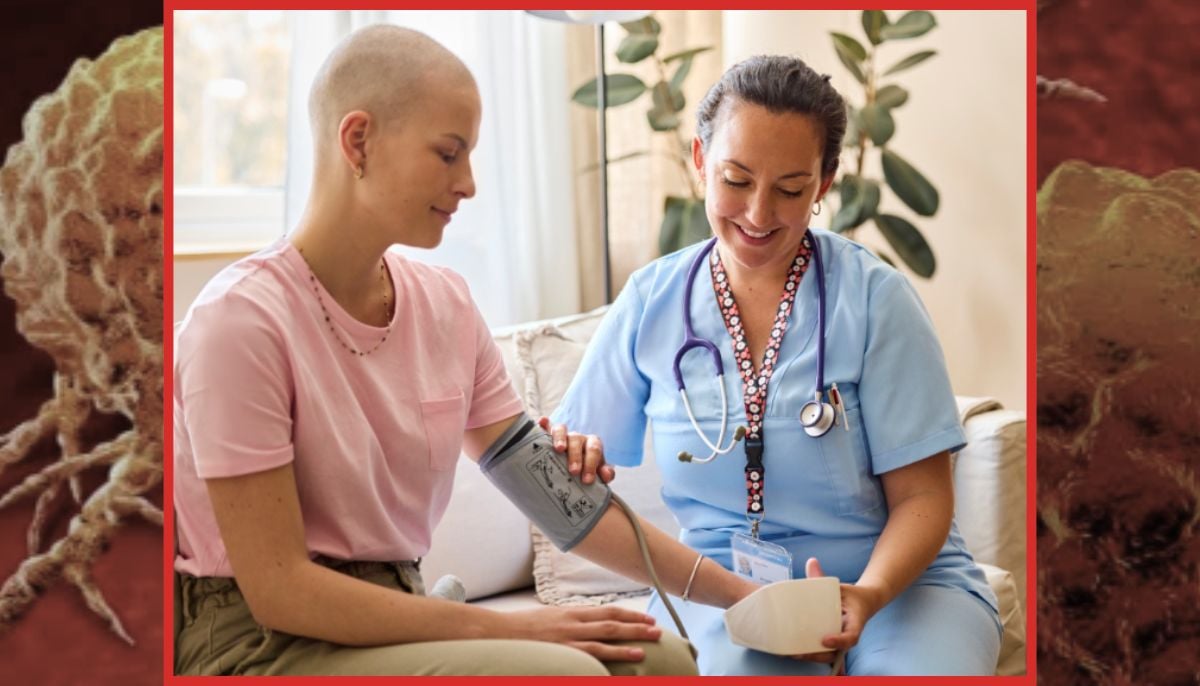
Doctors have found that a new breakthrough therapy has reversed incurable blood cancers in some patients.
A therapy that would once have been considered a piece of science fiction has reversed aggressive blood cancer in some patients.
As the doctors report, the treatment involves precisely editing the DNA in white blood cells to convert them into a cancer-fighting “living drug.”
Leukemia, or blood cancer, is one of the most common cancers, especially in children.
It occurs due to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, infections and bleeding, but it is often highly curable with early treatment.
Doctors have exceptionally unveiled a cure for the impossible treatment of cancer as a kind of ‘gene therapy’ called BE-CAR7.
Response to trial in patients:
Patients who received it saw their first tests, saw their cancer disappear completely, and remained cancer-free for years.
Experts say this could be a major turning point in the treatment of blood cancer.
Leukemia is a blood cancer that starts in the bone marrow, where blood cells are made, and one of its aggressive forms is called ‘T-cell leukemia’.
T cells are supposed to be the body’s guardians – seeking out and destroying threats – but in leukemia they grow abnormally out of control.
As reported by BBC, The first girl to receive BE-CAR7 treatment was a 13-year-old girl whose cancer left no trace within 28 days of treatment and remained free of the disease as of 2022.
Following her successful treatment, the study was then expanded to treat two more adults and eight children with T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia, with almost two-thirds (64%) of patients in remission.
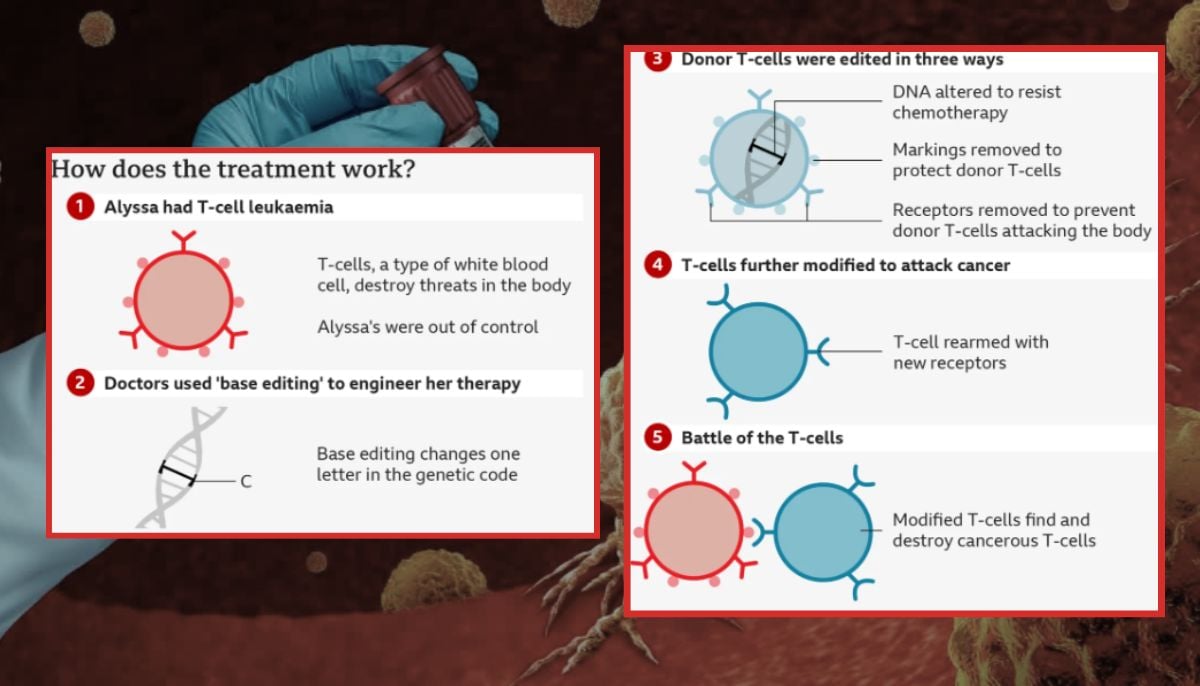
How the new treatment works:
With the BE-CAR7 treatment, doctors use healthy immune cells from a donor that are carefully changed in the laboratory using a precise gene editing method. Scientists are making three major changes:
The cells are changed so that the patient’s body does not reject them and cannot attack each other.
These cells are trained to recognize and kill cancer cells, and once injected into a patient’s body, they act like a living drug, seeking out and destroying cancer cells in the blood.
The team of doctors from University College London UCL and Great Ormond Street Hospital used technology to treat blood cancer called ‘base editing’.
The four types of bases in DNA – adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) – are the building blocks of our genetic code, and billions of bases in our DNA are the manual for our body.
The base editing method allows scientists to zoom in on a specific part of the genetic code and then change the molecular structure of just one base, converting it from one type to another and rewriting the manual.
The newly discovered treatment for blood cancer evaluates that researchers wanted to harness the natural power of healthy T cells to detect and destroy threats and turn them against the T cell acute lymphocytic leukemia.