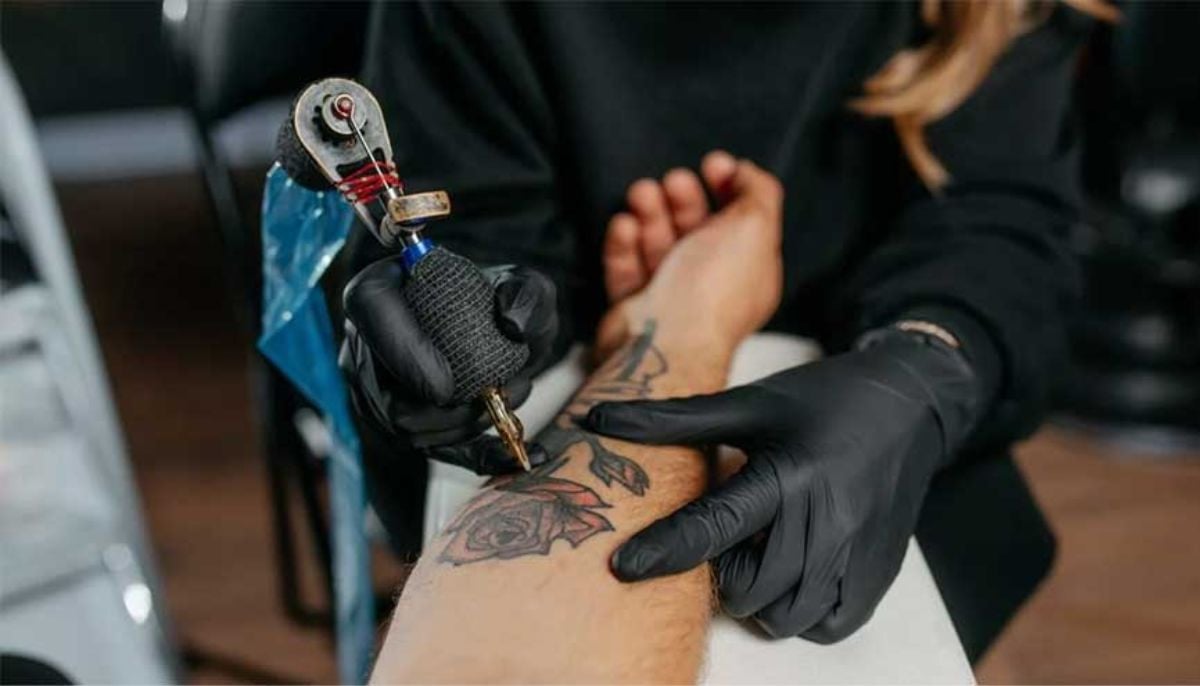
A new study has found that people with tattoos had a 29% higher risk of developing melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer linked to ultraviolet (UV) exposure.
Tattoos primarily did not appear to increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma, another form of cancer associated with UV damage.
It has been observed that both cancers share a common risk factor but arise from different cell types and differ in severity, with melanoma considered more dangerous.
Melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma developed gradually and are rare, making research challenging.
The study, known as a case-control study, was conducted on people who had already been diagnosed with cancer to investigate tattoos.
The National Cancer Register identified everyone between the ages of 20 and 60 who was diagnosed with melanoma in 2017.
Furthermore, questionnaires were sent to all participants asking about decorative tattoos, permanent makeup and medical tattoos, as well as their size and location, to determine whether the tattooing occurred before or after developing cancer.
The results showed that people with tattoos were 29% more likely to develop melanoma than people without tattoos.
On the contrary, the risk increase seemed greatest among those who had had tattoos for more than ten years.
People with tattoos are advised to protect their skin from UV rays to prevent excessive tanning.